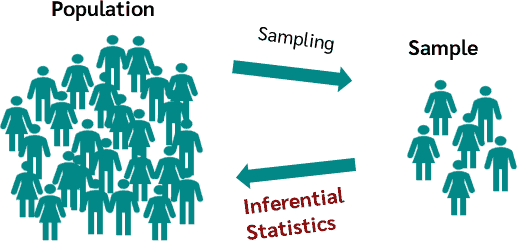
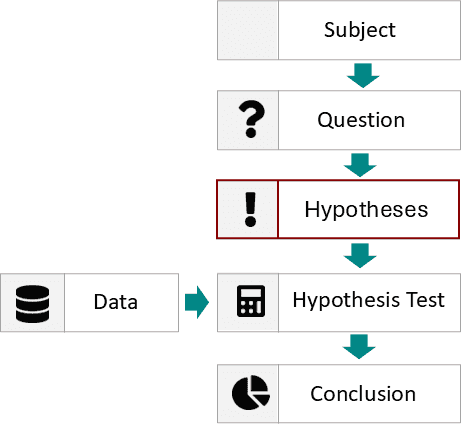
In statistics, a p-value of 0.05 (or less) is commonly used as a threshold for determining statistical significance.
A low p-value means that very low chance of such result. Something must be going on.
A large p-value (> 0.05) means that high chance of such result. You accept the null hypothesis. There is nothing here.
Is a p-value of 0.0501 really that different than a p-value of 0.0499? No. Life is filled with shades of gray, we sometimes have to make yes/no decisions and we have to choose a dividing line somewhere.
A defined significance level (often 5%), but can be adjusted to higher or lower.
Level of significance (alpha) is a fixed limit that is determined in advance. The level of significance does not depend on our observations and is not calculated, it is a decision determined on circumstances and study power.
If the p-value is 3%, for example, then it is only 3% likely that it occur at random.
One-tail p value
- P-value from Z score
- P-value from t score
- P-value from chi-square score
- P-value from F-ratio score
- P-value from Pearson (r) score
- P-value from Tukey q (studentized range distribution) score

What is Null hypothesis?
A hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. It is all due to randomness. Effect does not exist.
Null hypothesis is denoted as H0.
What is opposite of null hypothesis?
Alternate hypothesis is denoted as H1.